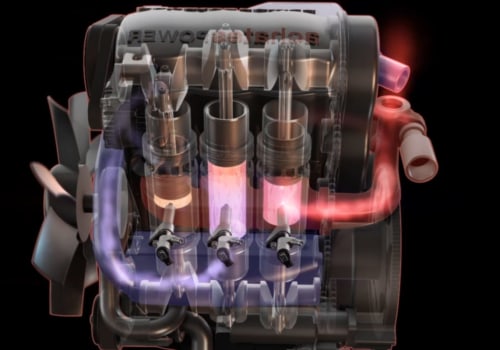
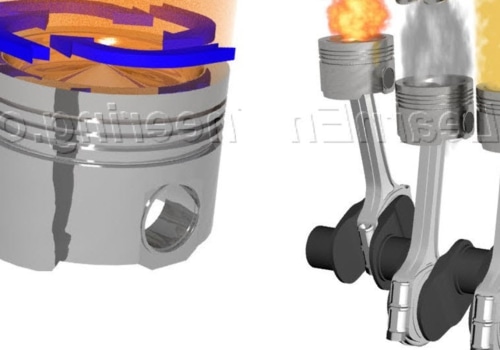
The diesel engine has become an integral part of the Navy's propulsion capabilities. It is a combustion system that transforms thermal energy into mechanical work, and is used to power a variety of vessels. Marine engineering is the discipline related to the engineering design process of marine propulsion systems, which have evolved from human-powered oars and sails to modern electric motors and internal combustion engines. The marine diesel engine is the main engine of the propeller for most modern merchant ships, such as container ships and VLCCs.
This configuration can achieve large power outputs and is characterized by operational reliability due to its simplicity. The alternative marine diesel engine was first used in 1903, when Branobel put the Vandal diesel electric river tanker into service. Combined cycles, such as gas turbines, may have higher thermal efficiency than diesel engines alone; however, the type of fuel needed for these gas turbines is much more expensive than that needed for diesel engines, so operating costs are even higher. The importance of diesel engines in marine propulsion cannot be overstated.
They are reliable, efficient, and cost-effective, making them an essential part of the Navy's propulsion capabilities.